Some may describe it as their passion, while others may consider it a stress reliever or a part of their daily life. In every form, listening to music has become an inseparable part of our lives. Music plays different roles in our lives.
Sometimes it makes us enjoy ourselves with enthusiasm; sometimes it makes us feel pleasant and good. Other times, it reminds us of someone or some feel-good moments from our past. Listening to music has sustained generations, but the medium has changed.
Earlier, people relied on radios to listen to music, while the present generation has iPods, smartphones, PCs, and other gadgets for that purpose. When it comes to PCs, we have dedicated software called music players to play our choice of songs or playlists.
While most generations have smartphones and iPods to listen to music, these software applications are also a common source for enjoying music that suits the mood of people who spend hours working on PCs and laptops and find it convenient to listen using their daily companions.
Table of Contents
- 1 Music Players and Linux
- 2 21 Best Music Players on Linux to Date
- 3 7. Kew
Music Players and Linux
The growth of Linux as an accepted operating system in the market was not significant a few decades ago, but the flourishing of this open-source industry in the IT sector over the past few years has created tremendous opportunities for many professionals who want to contribute to this industry with their work.
One such opportunity arose in the late twentieth century with the need for a Music Player on Linux. Since then, many music players have been added to various Linux distributions, some as defaults and others as externally downloadable options.
The main aim of any music player is to support all audio file formats compatible with both Windows and Linux, as well as to provide support for online music streaming, which is trending nowadays.
21 Best Music Players on Linux to Date
Below, we list some of the best music players created on Linux to date. A music player can be characterized as the best by considering the following features: supported formats, memory consumption, online or offline streaming (or both), user interface design, and feature set.
Some of the music players highlighted below guarantee all the above factors, while others guarantee only some of these factors.
1. VLC Media Player
VLC Media Player is a free, open-source multimedia player that works on various platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android. It can play almost any type of media file, such as videos, music, DVDs, and streaming content without needing additional codec packs.
VLC is known for its simplicity, speed, and powerful features. Users can customize it with skins and extensions. Importantly, VLC is completely free of spyware and ads, ensuring a user-friendly experience without tracking. Overall, it is a versatile tool for anyone looking to play multimedia files easily and effectively.
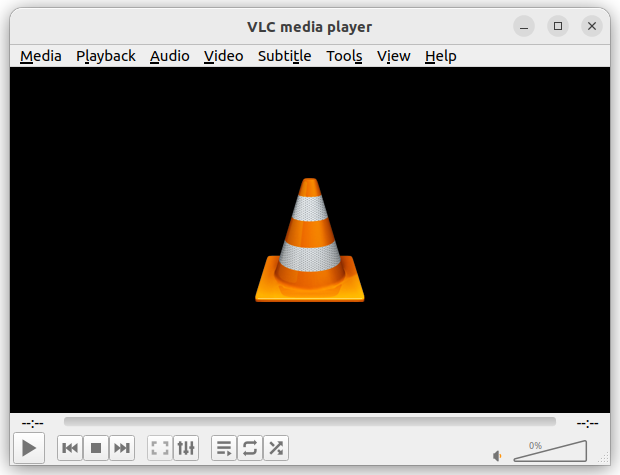
Install VLC in Linux
To install VLC on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install vlc [On Ubuntu 24.04, Debian 13] sudo yum install vlc [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/vlc [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add vlc [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S vlc [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install vlc [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install vlc [On FreeBSD]
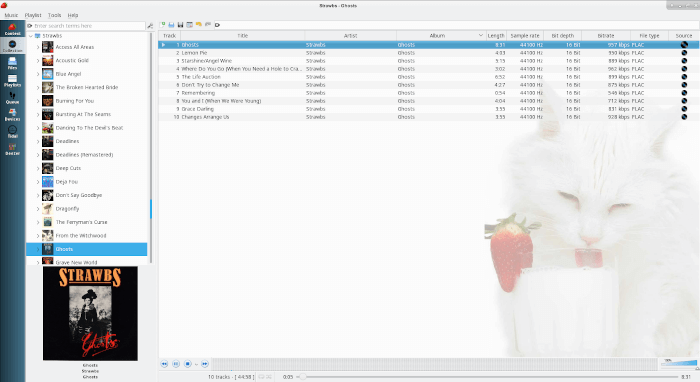
2. Strawberry Music Player
Strawberry is a free music player and organizer designed for music collectors and audiophiles, which allows users to play digital music, manage collections, and stream online radio.
Developed as a fork of Clementine, Strawberry is built using C++ with the Qt framework and GStreamer. While it’s primarily available for Linux, macOS and Windows versions require a monthly sponsorship for access.
Strawberry also supports features like album cover management and streaming from services like Tidal. The project is open-source, inviting community participation in its development and maintenance.
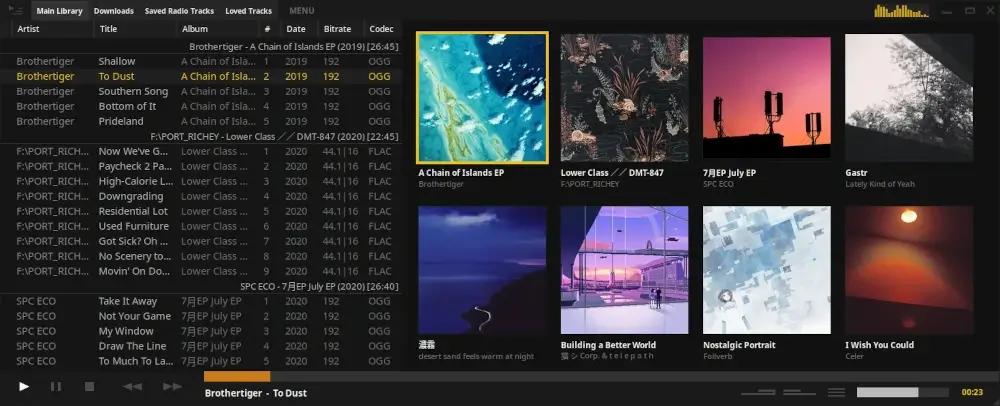
3. Tauon
Tauon Music Box is a modern, free, and open-source music player designed for Linux desktop users that allows you to easily manage and play your music collection with features like drag-and-drop playlist creation, gapless playback, and support for various audio formats, including FLAC.
The player also integrates with services like Spotify and Last.fm, enabling you to scrobble tracks and manage playlists seamlessly. Additionally, it offers network playback options and a user-friendly interface, making it a versatile choice for music enthusiasts looking for a streamlined listening experience.
Install Tauon in Linux
The recommended way of installing Tauon is through Flatpak.
flatpak install flathub com.github.taiko2k.tauonmbflatpak run org.kde.elisa flatpak run com.github.taiko2k.tauonmb
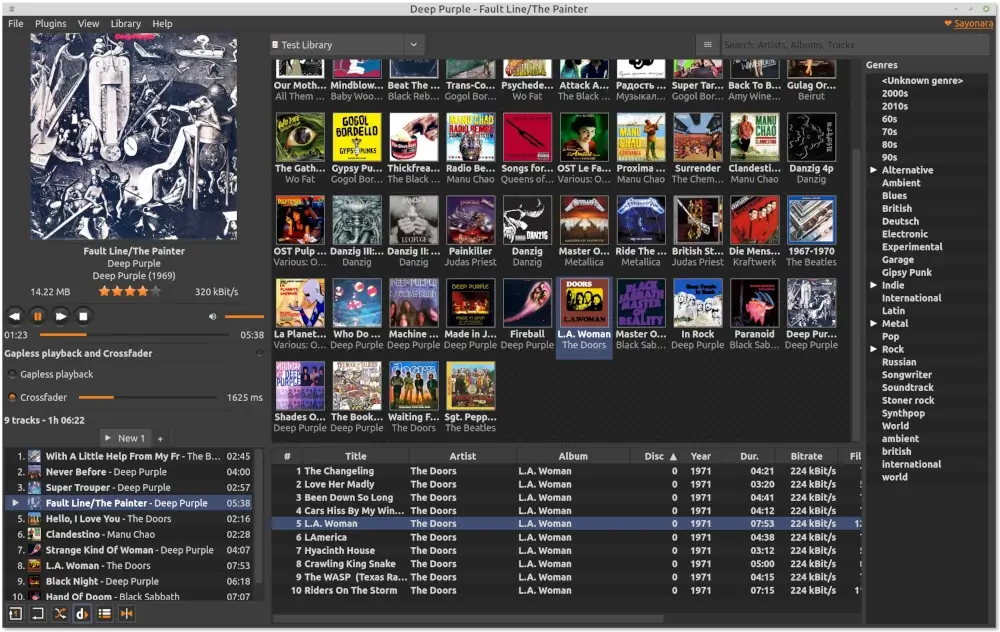
4. Sayonara Player
Sayonara is a highly customizable, open-source audio player written in C++ and supported by the Qt framework, which uses GStreamer as its audio backend and is available for Linux and BSD operating systems.
Sayonara offers a clean and fast user interface, with optional features that can be removed or hidden based on user preferences. It provides various ways to manage and organize large music collections, including artist, album, and track table views, an album cover view, and a directory tree view.
Users can create playlists and take advantage of dynamic playback, which automatically adds similar tracks to the playlist. Sayonara also supports plugins that provide additional functionality, such as a spectrum analyzer, equalizer, and crossfading.
Install Sayonara in Linux
To install Sayonara on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install sayonara [On Ubuntu 24.04, Debian 13] sudo yum install sayonara [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/sayonara [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add sayonara [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S sayonara [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install sayonara [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install sayonara [On FreeBSD]
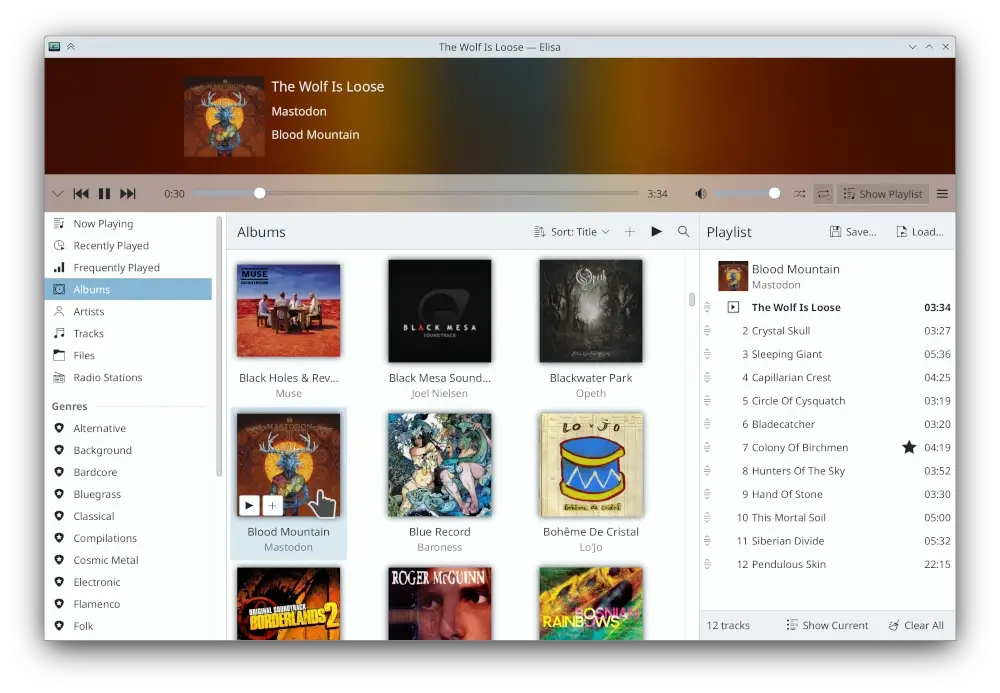
5. Elisa
Elisa is a user-friendly music player created by the KDE community that allows you to easily browse your music collection by genre, artist, album, or track.
You can also listen to online radio, create playlists, and view lyrics. The player features a “Party Mode” that showcases album art prominently. Elisa adapts to your desktop’s color scheme on KDE Plasma but also offers standard light and dark modes.
It is available for Linux and can be installed through various application stores like Flathub.
Install Elisa on Linux
The recommended way of installing Elisa is through Flatpak.
flatpak install flathub org.kde.elisa flatpak run org.kde.elisa
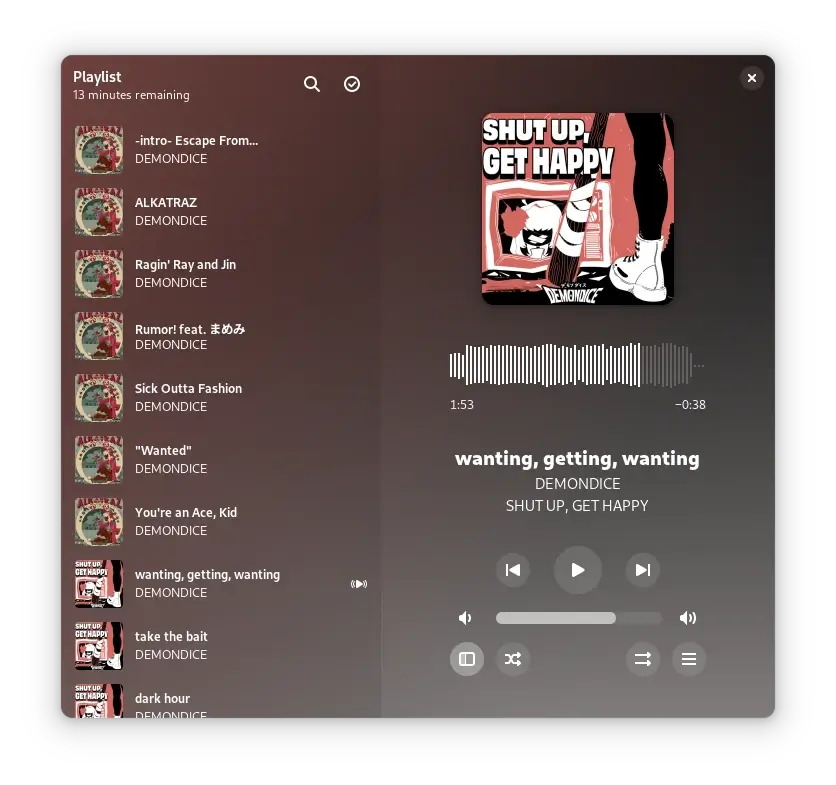
6. Amberol
Amberol is a music player tool designed for the GNOME desktop environment that focuses on simplicity and ease of use, allowing users to play audio files effortlessly.
The tool supports various audio formats and offers a clean interface for managing playlists. Amberol is developed as an open-source project, meaning anyone can contribute to its improvement.
It aims to provide a lightweight alternative to more complex music players, making it suitable for users who prefer straightforward functionality without unnecessary features.
Install Amberol on Linux
The recommended way of installing Amberol is through Flatpak.
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo flatpak install flathub io.bassi.Amberol
7. Kew
kew is a command-line music player designed for Linux environments, enabling users to listen to music directly in the terminal.
It supports various audio formats, including MP3, FLAC, and OGG, and features capabilities such as playlist creation, gapless playback, and library searching with partial titles.
Users can control playback with simple commands and customize settings via a configuration file. Installation options include package managers like APT for Debian/Ubuntu and AUR for Arch Linux.
The tool emphasizes privacy, as it does not collect user data, making it a suitable choice for those looking for a lightweight and efficient music player.

Install Kew in Linux
To install Kew on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install kew [On Ubuntu 24.04, Debian 13] sudo yum install kew [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/kew [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add kew [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S kew [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install kew [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install kew [On FreeBSD]
8. Amarok
Amarok is a cross-platform open-source software application written in C++ (Qt) and released under the GNU Public License.
Originally started by Mark Kretschmann as an effort to improve XMMS, this software was initially named amaroK, after the name of a wolf, and was later changed to Amarok.
It can play media files in various formats, including but not limited to FLAC, Ogg, MP3, AAC, and Musepack. Apart from playing offline collections, it can stream online music by integrating with various services like Magnatune, Jamendo, MP3tunes, Last.fm, and Shoutcast.
In addition to basic services, Amarok provides advanced features such as fetching music, transferring music to or from digital music players, moodbar support, and dynamic playlist support.
Install Amarok on Linux
To install Amarok on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install amarok [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install amarok [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/amarok [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add amarok [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S amarok [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install amarok [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install amarok [On FreeBSD]
9. Clementine
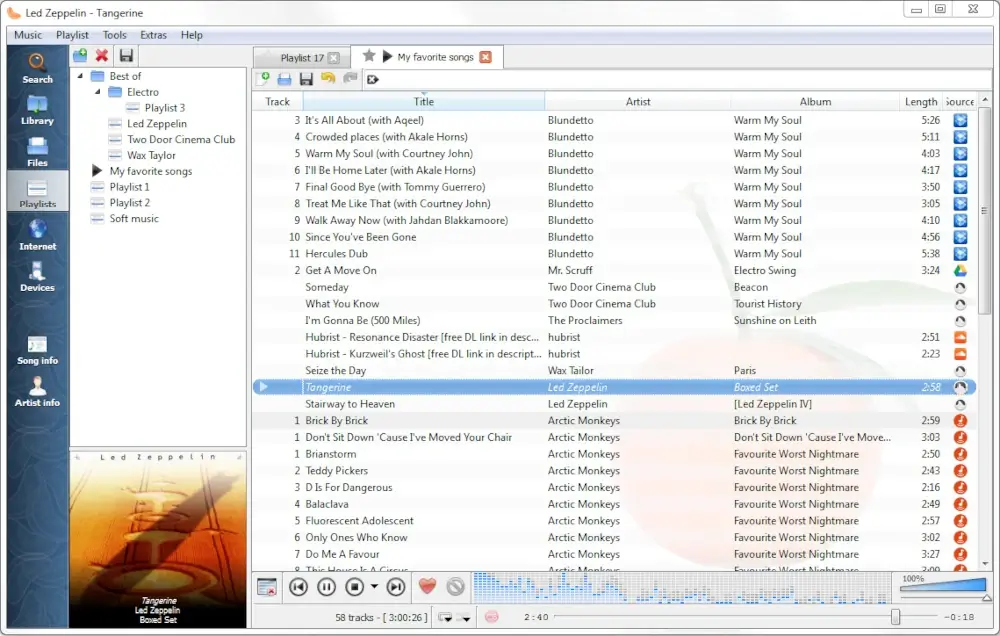
Released in February 2010, Clementine is a cross-platform software designed to address the criticism surrounding the transition of Amarok from version 1.4 to 2.0.
Clementine is a port of Amarok version 1.4 to the Qt4 and GStreamer multimedia frameworks. It is written in C++ (using the Qt framework) and released under the GNU General Public License.
With features similar to those of Amarok, Clementine offers additional functionalities such as remote control using an Android device, Wii Remote, MPRIS, or a command-line interface.
Install Clementine in Linux
To install Clementine on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install clementine [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install clementine [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/clementine [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add clementine [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S clementine [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install clementine [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install clementine [On FreeBSD]
10. Lollypop
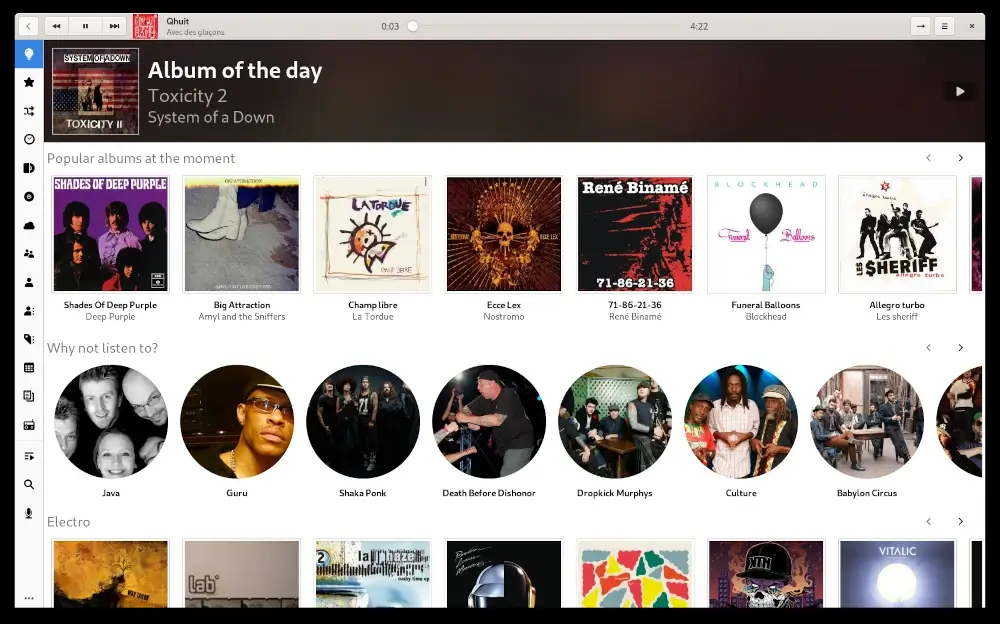
Lollypop is a GNOME music player that is a free and open-source project hosted on GitHub. It is written entirely in Python and Gtk3.
It is very lightweight and has a visually appealing user interface with the ability to play MP3, MP4, OGG, and FLAC files. It provides features to read artist biographies from Last.fm or Wikipedia and lyrics of the songs from Wikia.
Additionally, it offers features like browsing through the collection by artist, album, or genre, and a party mode effect for playing music. This player can only play downloaded audio tracks and does not allow streaming audio.
Install Lollypop on Linux
To install Lollypop on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install lollypop [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install lollypop [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/lollypop [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add lollypop [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S lollypop [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install lollypop [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install lollypop [On FreeBSD]
11. Cmus
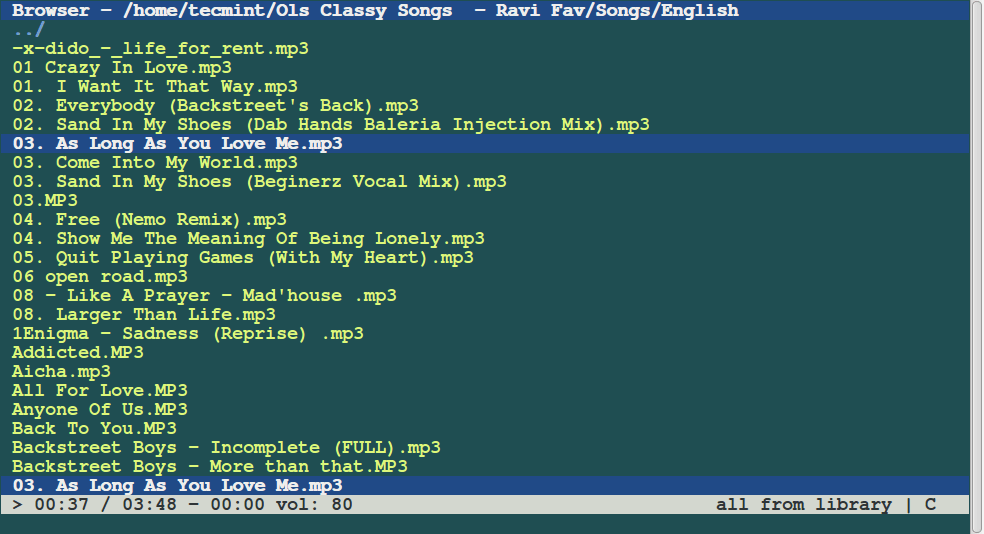
Cmus is a console-based music player for Linux operating systems. Written exclusively in C and released under the GNU General Public License, this music player runs in the terminal and is operated via the keyboard using commands prefixed with a colon.
Being console-based allows Cmus to load quickly, even with a large number of songs. It supports various audio formats, including Ogg, MP3, WAV, MPEG-4/AAC, and WMA.
While it benefits from the speed and efficiency of a console-based application, this also affects its user interface, which is not very glossy. Additionally, Cmus can be controlled through the cmus-remote program and is known to work on many Unix-like operating systems, such as FreeBSD, OpenBSD, and Cygwin.
Install Cmus in Linux
To install Cmus on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install cmus [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install cmus [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/cmus [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add cmus [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S cmus [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install cmus [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install cmus [On FreeBSD]
12. Aqualung
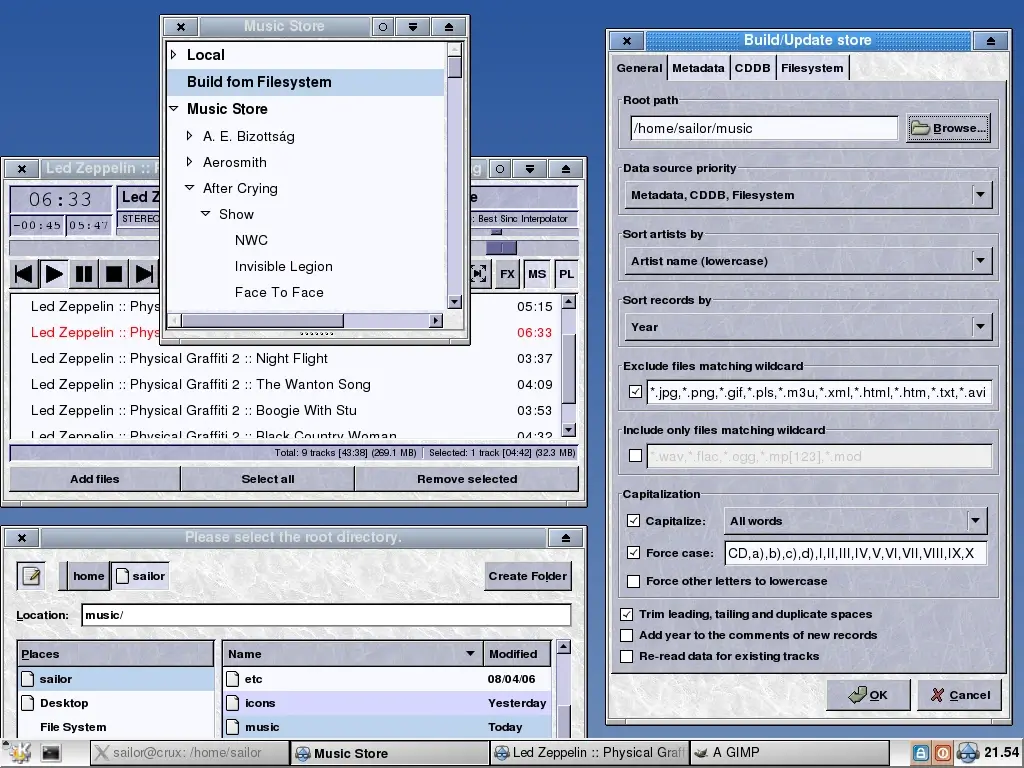
Released in August 2015, Aqualung is a cross-platform audio player originally targeted at GNU/Linux but also compatible with macOS, Windows, FreeBSD, and more.
It is written entirely in C and is available in multiple languages, including French, German, and Hungarian. This software supports various audio file formats, such as Ogg, Vorbis, FLAC, and MP3.
What sets it apart from most music players is its ability to play gapless music. Other features include multi-language support, the ability to manage multiple playlists simultaneously, customizable skins, support for MPEG formats, and the ability to play audio CDs.
Install Aqualung in Linux
To install Aqualung on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install aqualung [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install aqualung [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/aqualung [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add aqualung [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S aqualung [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install aqualung [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install aqualung [On FreeBSD]
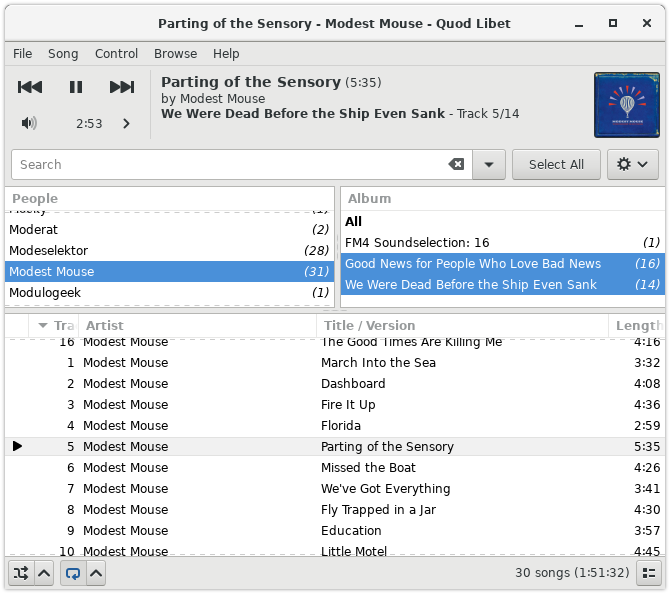
13. Quod Libet
Quod Libet is an open-source, cross-platform music player and tag editor. Written in Python using GTK+ and released under the GNU General Public License, this software supports Linux, Windows, and macOS, requiring plugins for Python and PyGObject, as well as OSS and ALSA-compatible audio devices.
With a user-friendly interface and Pango support for dynamically positioning tags, Quod Libet offers a variety of features, including support for audio backends via the GStreamer plugin, ReplayGain support, the option to shuffle the entire playlist before repeating, an extensive set of features for tag editing, saving the play count of songs, downloading lyrics, and fast-refreshing the entire library
Install Quod Libet in Linux
To install Quod Libet on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install quodlibet [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install quodlibet [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/quodlibet [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add quodlibet [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S quodlibet [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install quodlibet [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install quodlibet [On FreeBSD]
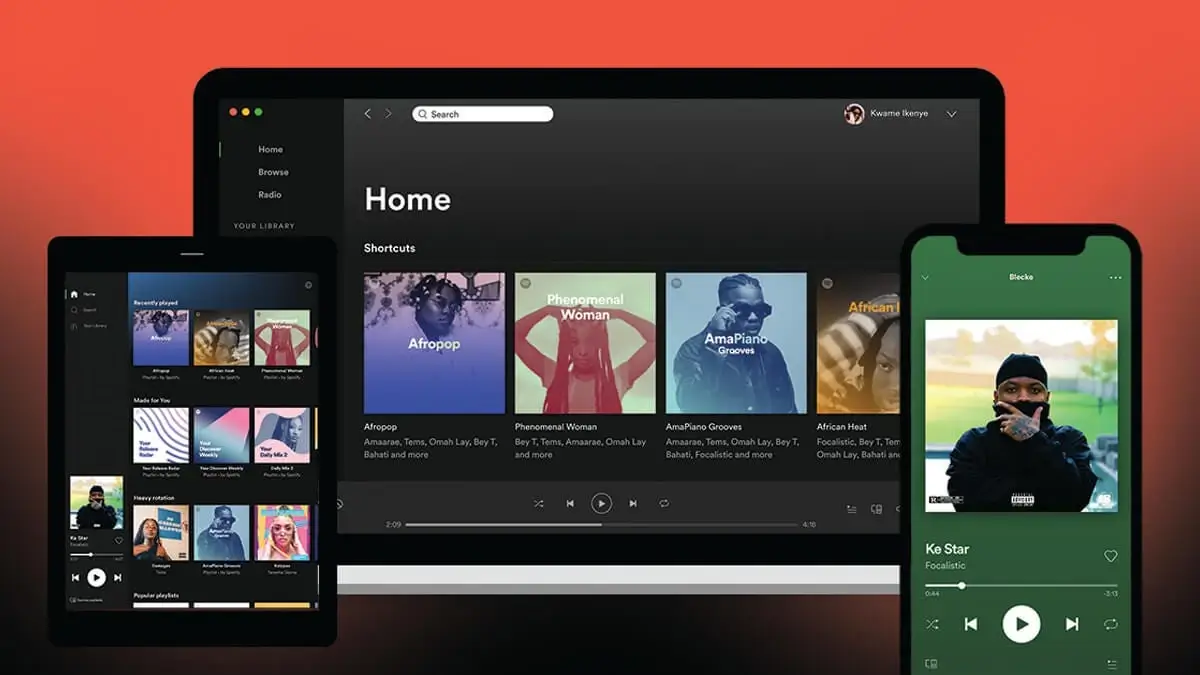
14. Spotify
Spotify is a Swedish commercial music streaming, podcast, and video service that provides users with an online audio player. It is a cross-platform service available on almost all devices.
Released in October 2008 by the Swedish startup Spotify AB, it quickly became popular, attracting over 10 million users. By June 2015, the platform had gathered a substantial user base of around 75 million, which included 20 million paying subscribers.
Currently, Spotify boasts 615 million monthly active users, with 239 million of those being paying subscribers, which reflects a substantial growth in both total users and subscribers over the past nine years.
Spotify allows users to browse or search for music by artist, album, genre, playlist, or record label. It offers two music streaming options: Spotify Free, with a bitrate of 160 kbit/s, and Spotify Premium, with a bitrate of up to 320 kbit/s.
Install Spotify in Linux
To install Spotify on Linux, use the snap package manager for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo snap install spotify
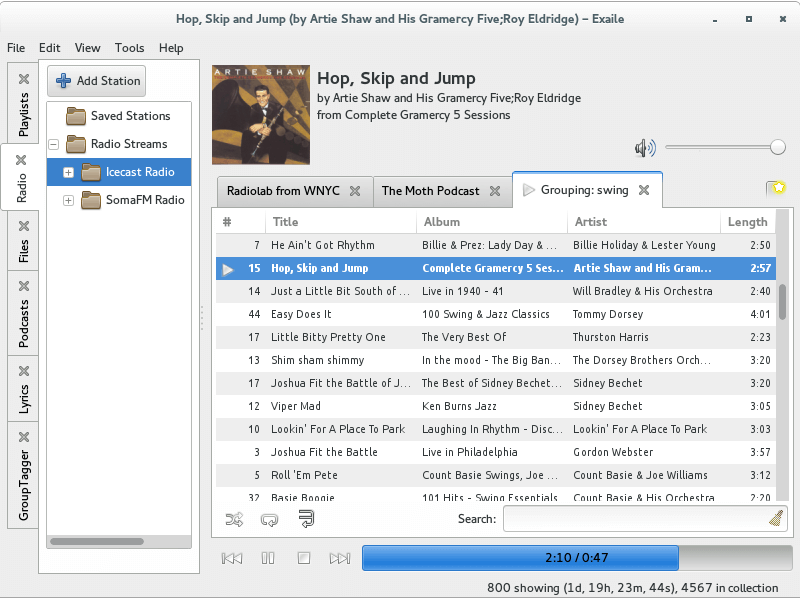
15. Exaile
Exaile is a cross-platform music player whose latest release, version 3.4.2, was in November 2014. It uses the GTK+ widget toolkit rather than Qt and is written in Python with the GStreamer media framework.
With a plain yet appealing user interface, this music player bears a strong resemblance to Amarok in many of its functionalities, including Last.fm support, fetching lyrics, and editing tags.
Additionally, it provides device support through external plug-ins. Beyond these basic features, it also includes advanced options like ReplayGain support, Moodbar integration, and the ability to preview tracks via a secondary sound card
Install Exaile in Linux
To install Exaile on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install exaile [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install exaile [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/exaile [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add exaile [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S exaile [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install exaile [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install exaile [On FreeBSD]
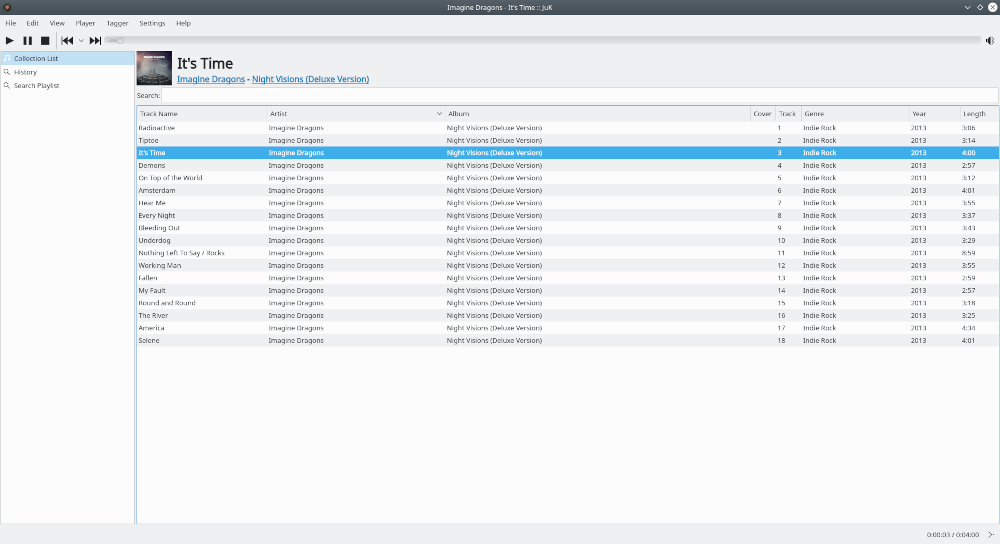
16. Juk
JuK is another cross-platform audio player designed for Unix-like systems and Windows, released in February 2004. It is written in C++ and is released under the GPL.
JuK supports a collection of audio files in formats like MP3, Ogg Vorbis, and FLAC. Some features that make it a part of this list include dynamic search playlists that are auto-updated, an auto-sync feature that automatically detects newly added songs in the music directory, and support for guessing tag information through online lookup, as well as tag reading and editing.
Install Juk on Linux
To install Juk on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install juk [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install juk [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/juk [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add juk [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S juk [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install juk [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install juk [On FreeBSD]
17. MPD
MPD, or Music Player Daemon, is a music player server written in C++, which was released in February 2015 and is available for Unix-like operating systems and Windows, distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Unlike other music players discussed so far, MPD operates as a daemon server that runs in the background and requires a client for user interaction. Once initiated, the daemon uses an in-memory database of audio files, allowing any local client to play back audio after connecting to the server via sockets.
MPD supports a wide range of audio file formats, including Ogg, Vorbis, FLAC, Opus, WavPack, MP3, and MOD. Although it operates as a daemon and lacks a built-in user interface, it offers various features such as buffer support for playback, seeking and crossfading capabilities, and remote control over the network.
Additionally, it supports multiple audio output systems including ALSA, OSS, JACK, and PulseAudio, and is compatible with OS X and Windows. While MPD itself does not provide a complex user interface, there are several clients available that offer simple interfaces for users to interact with the daemon
Install MPD in Linux
To install Juk on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install mpd [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install mpd [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/mpd [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add mpd [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S mpd [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install mpd [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install mpd [On FreeBSD]
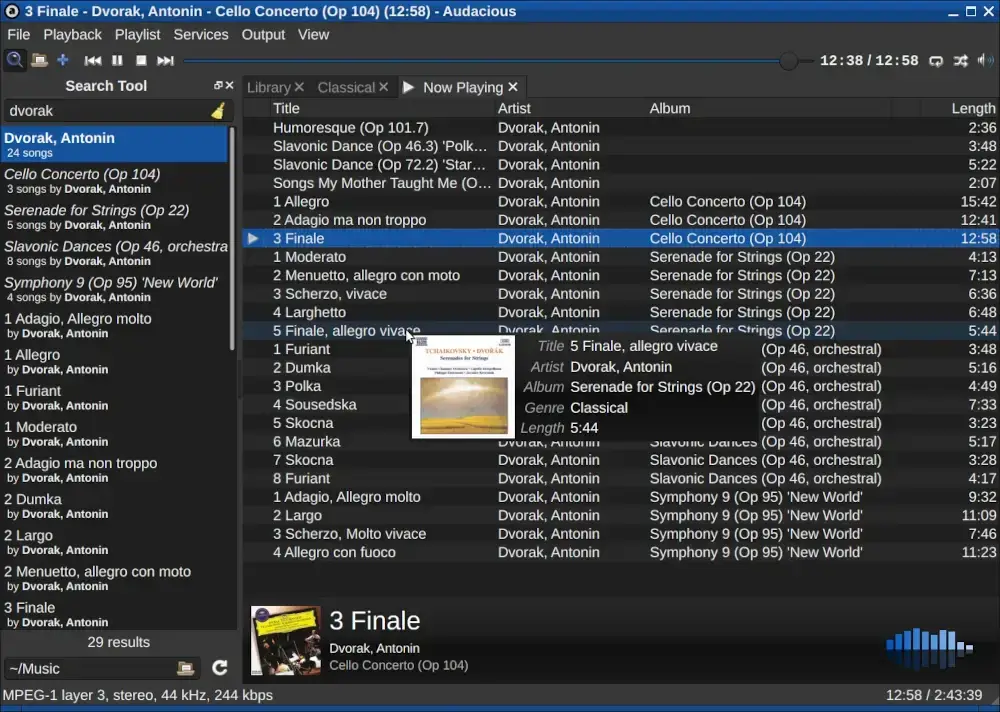
18. Audacious
Primarily designed for POSIX-compatible platforms like Linux, with added support for Windows, Audacious is an open-source audio player and the default music player for Lubuntu and Ubuntu Studio. It is entirely written in C++, with the latest version being 4.4, released in July 2024.
Audacious offers a wide variety of features, most of which are available through external plugins, including Decoder, Transport, Output, and Effect plugins. Additionally, it supports a wide range of codecs, including MP3, FLAC, WavPack, TTA, Shorten, and MIDI.
The player has full support for Winamp 2 skins, with all skins typically rendered in PNG format, allowing users to adjust the RGB color balance themselves. Although it is a standalone player, it accepts connections from client software like Conky
Install Audacious on Linux
To install Audacious on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install audacious [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install audacious [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/audacious [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add audacious [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S audacious [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install audacious [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install audacious [On FreeBSD]
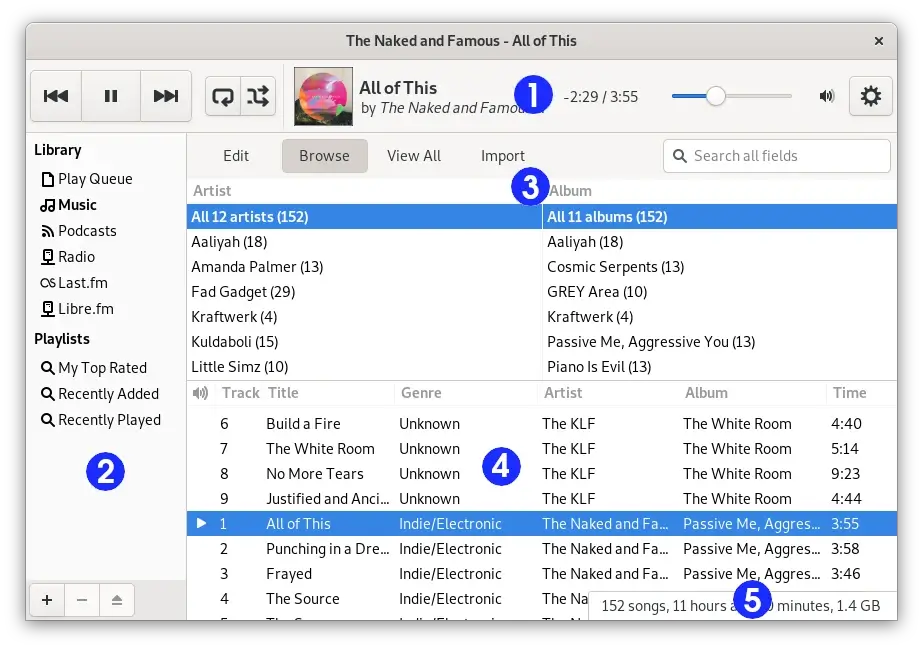
19. Rhythmbox
Written in C and released for Unix-like systems such as BSD, GNU/Linux, and Solaris, Rhythmbox is an audio player that plays and helps organize digital music. It is the default music player for Ubuntu Linux systems and works well under the GNOME desktop environment with the GStreamer media framework.
With a visually appealing user interface, Rhythmbox provides various features such as gapless playback, Last.fm support (which allows it to stream online music), audio CD burning, and music importing.
It can integrate efficiently with numerous platforms. Versions of Rhythmbox above 0.10.0 support DAAP sharing. Additionally, it uses the udev subsystem of Linux to detect the device selected for playing music
Install Rhythmbox in Linux
To install Rhythmbox on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install rhythmbox [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install rhythmbox [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/rhythmbox [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add rhythmbox [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S rhythmbox [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install rhythmbox [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install rhythmbox [On FreeBSD]
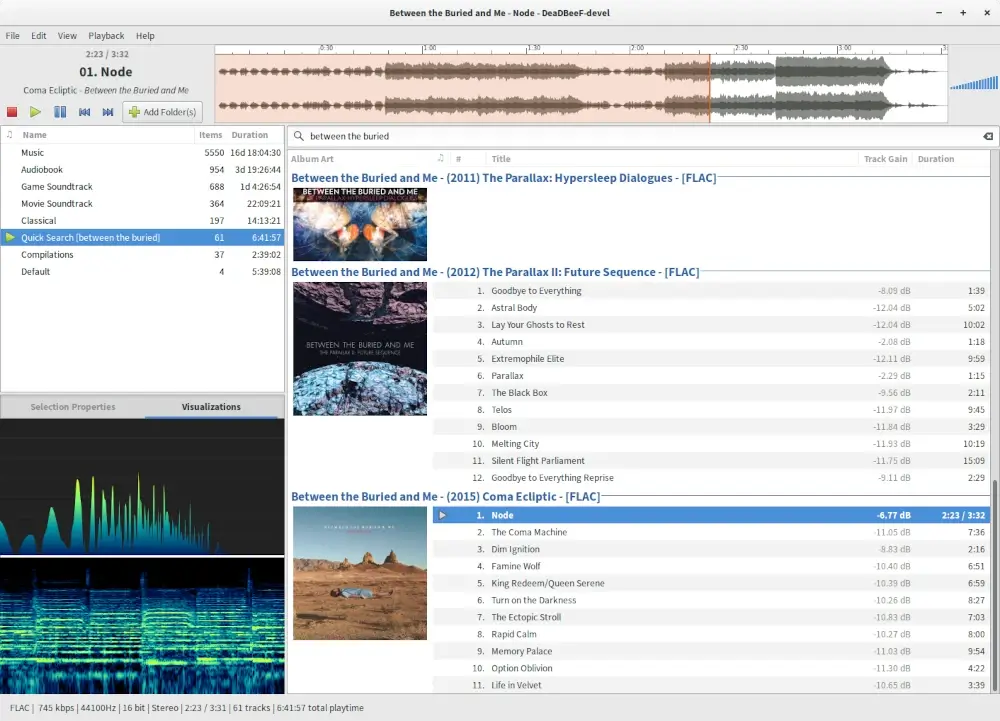
20. DeaDBeeF
Written in C, DeaDBeeF is a lightweight yet powerful music player released under the GPLv2 for Linux and Android. Most of the external plugins supported by DeaDBeeF are written in C++, and the interface uses GTK2.
One of the major advantages it has over many audio players is its low memory consumption. It can play a wide variety of formats, including but not limited to MP3, Ogg, WAV, and M4A.
Other notable features include online and offline streaming of music, 18-band equalizer support, gapless playback, cue sheet support, and Last.fm support.
Install DeaDBeeF in Linux
To install DeaDBeeF on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install deadbeef [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install deadbeef [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/deadbeef [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add deadbeef [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S deadbeef [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install deadbeef [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install deadbeef [On FreeBSD]
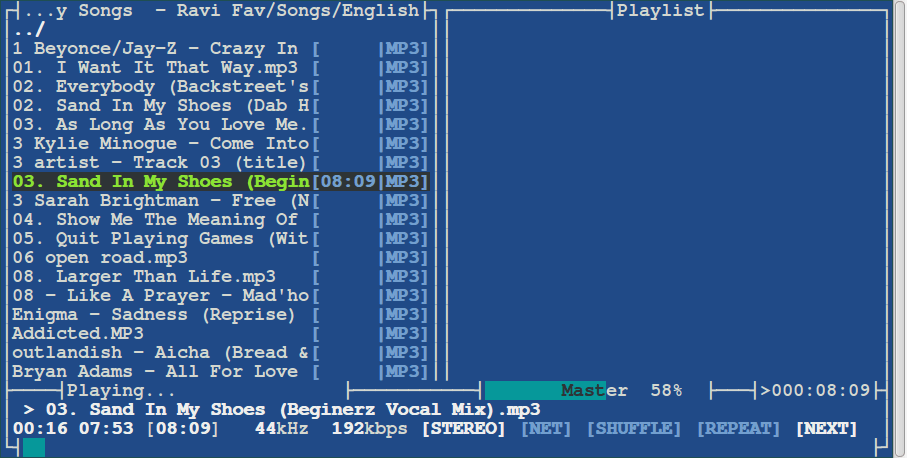
21. MOC (Music On Console)
MOC is another text-only music player somewhat similar to MPD but with some changes. Written in C and based on ncurses, this console audio player is specifically designed for Linux/Unix-based systems. It was originally developed by Damian Pietras and is currently maintained by John Fitzgerald.
The console-based nature of this audio player offers several advantages, including a simple yet powerful interface and low memory utilization. Additionally, it has a separate thread for the output buffer, which helps it avoid high-load situations.
MOC features customizable interface layouts and supports ALSA, OSS, and JACK outputs. Like MPD, it also has a client/server architecture, but it does not support remote network accessibility through any graphical client.
Install MOC in Linux
To install MOC on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install moc [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install moc [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/moc [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add moc [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S moc [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install moc [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install moc [On FreeBSD]
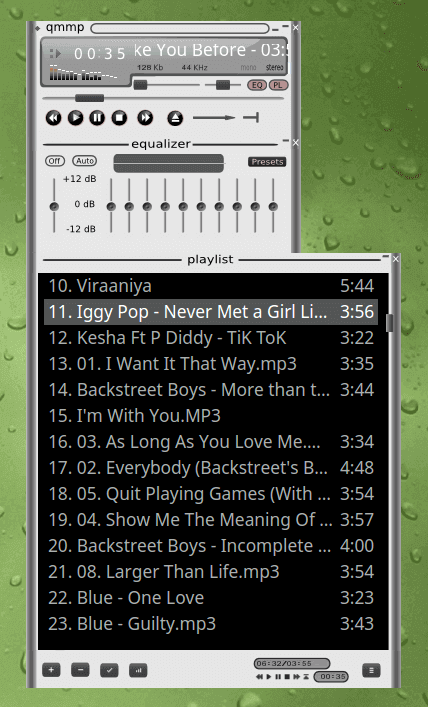
22. Qmmp Music Player
Qmmp is a cross-platform, Qt-based audio player similar to Audacious and Winamp. It is easily available for almost all Linux distributions without compilation unless you need the latest build.
It supports a wide variety of audio formats, including FLAC, Ogg Vorbis, MPEG-1, and AAC, along with support for cue sheets. It can have skins similar to Winamp, and you can even customize your skins.
Qmmp also supports volume normalization, which is a built-in option. Many other features can be accessed in this player using external plugins. Additional features include Last.fm support, ReplayGain support, viewing lyrics, crossfade, and support for ALSA, OSS, and JACK audio outputs.
Install Qmmp in Linux
To install Qmmp on Linux, use the following appropriate command for your specific Linux distribution.
sudo apt install qmmp [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install qmmp [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a sys-apps/qmmp [On Gentoo Linux] sudo apk add qmmp [On Alpine Linux] sudo pacman -S qmmp [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install qmmp [On OpenSUSE] sudo pkg install qmmp [On FreeBSD]
We have made this list based on our research. If you think of any other music player on Linux which should have been listed here then you can mention its name in the comments.