I feel that updates in Fedora are more frequent than those in other distributions like Ubuntu LTS. So, you need to update your system regularly.
If you are in a place with limited to no internet connection, upgrades will be pending for a significant time, which is not an ideal condition for a healthy system.
I had come across a Reddit discussion that Fedora had a mechanism for offline updates. I gave it a try and now I am sharing my findings with you.
🚧
This is not a “how to do this” kind of tutorial you usually see on It’s FOSS. This is more of me sharing my experiment with you so that you can derive a few learning points from my experience. Please don’t go blindly following things here.
I am going to discuss two scenarios:
- Offline updating Fedora system with limited internet connectivity: Here, you can at least update the package cache to see what installed packages can be updated. Works if you have a system running on limited mobile data.
- Offline updating a Fedora system that has no internet connectivity: Here, you have no clues on what packages can be updated. So, you make a list of all installed packages and download updates for all of them.
Both scenarios follow pretty much the same steps. You download the package updates on another Fedora system that can be connected with internet and then transfer the downloaded updates to the offline Fedora system via a USB.
Both offline and online Fedora systems should be running the same Fedora version.
Table of Contents
Scenario 1: For Systems with limited internet connectivity
📋
You’ll need another computer with Fedora installed that has an active and healthy internet connection or a Laptop with Fedora that can be moved to a place with better connectivity.
In this case, I assume that you have a limited metered network like the mobile internet. This can result in an efficient update, as you will be able to get some details about the package status of your system and the repositories.
🚧
I did not test the scenario for package updates from RPM fusion and externally configured repo packages like Brave browser. I only had packages installed only from the default Fedora repos.
Creating the list of packages to update
First, on the offline system, I got the details of all installed packages that required an update.
This can be done in a terminal by using the command:
dnf repoquery --upgrade --queryformat '%{name}.%{arch}' > updates.txt
Let’s view the contents of the file using the command:
less updates.txt
It contained a list of packages that required an update.
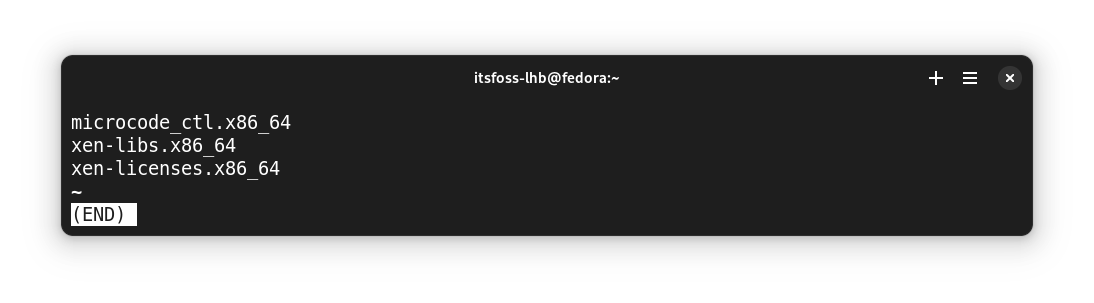
Downloading the update packages in a separate system
Next, on a Fedora system with sufficient internet connection, I created a folder in the download directory called “downloaded-packages”:
mkdir -p ~/Downloads/downloaded-packages
Now, with the command below, I downloaded the update packages.
dnf download --resolve $(cat updates.txt) --downloaddir="/home/$USER/Downloads/downloaded-packages"
It downloaded all the packages in the updates.txt file to the specified directory.
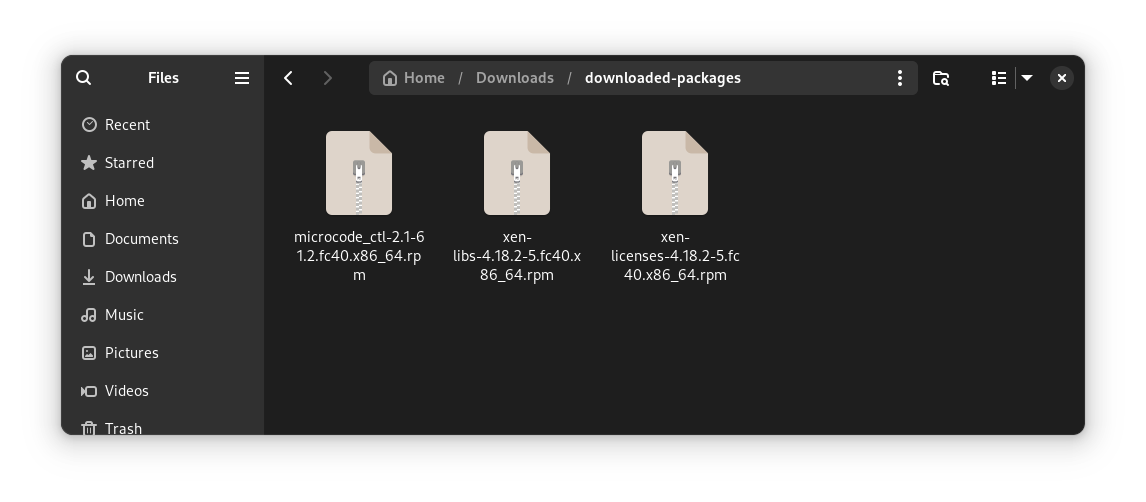
Then I copied this directory to a USB drive.
Installing the downloaded package updates
Now, on the offline Fedora system, I plugged in the USB with updated packages to the offline Fedora system.
I copied the downloaded-packages folder from the USB to the Downloads folder on the system.
Now, I switched to this copied directory:
cd ~/Downloads/downloaded-packages
And installed the updates on packages with:
sudo dnf install *.rpm
Method 2: For systems with no internet connection
Now, consider the situation where you have a system with no internet connection at all, but you can access the internet in some other places.
🚧
This method also needs a Fedora system that can access the internet, to download the actual package files. And it is also a method that can go wrong in many places. Use it with utmost caution and only if there is no other way.
List of all installed packages
In this method, I listed all the packages installed on the system and saved it to a file:
rpm -qa --queryformat "%{NAME}n" > packages.txt
This was a huge list with all the packages installed on the system.
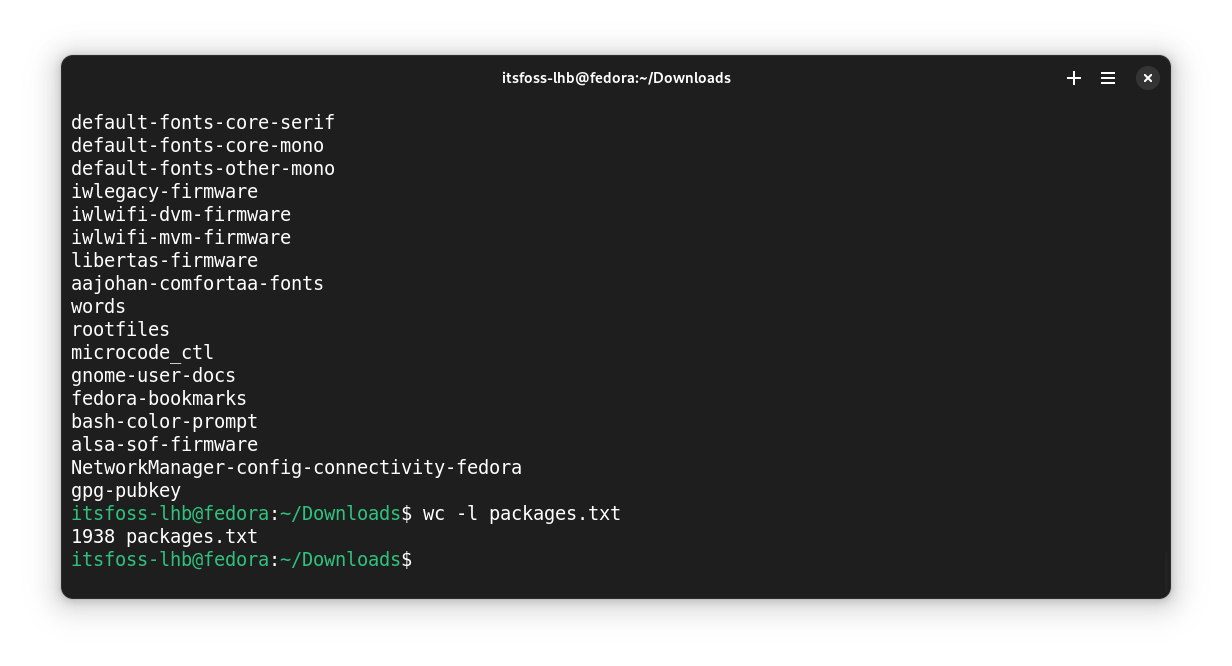
🚧
In the above screenshot, you can see the last entry as gpg-pubkey. This item has given me an error later, that say no package available in that name.
I copied this file to a USB and moved it to the system that can access the internet.
Download all packages
On the Fedora system with an internet connection, I downloaded all the packages using the command:
dnf download --resolve $(cat packages.txt) --downloaddir="/home/$USER/Downloads/downloaded-packages"
I copied the folder to a USB and then moved it to the Downloads folder on the offline system.
Update the offline system
After copying all the required files to the local system, I moved inside that directory and install those packages using the command:
cd ~/Downloads/downloaded-packages
sudo dnf install *.rpm
This will install all the packages from the list.
Conclusion
You may use --disablerepo=* option to disable checking the repo and mirrors. Use this option with caution.
Moreover, it is important to note that Fedora is not a system known for working entirely offline. You may find errors specific to your particular system as well.
Thankfully, we now have internet connection available in most parts of the world. And operating systems these days are geared to be used with an active internet connection.
Still, in some rare cases, computers do work offline. Although, Fedora is not the ideal operating system for such scenario.