PHP is the most popular scripting language used to create dynamic websites. With the release of PHP 8.4, developers can enjoy a host of new features and improvements that enhance performance and provide additional functionality for web applications.
If you want to use PHP 8.4 with Apache or Nginx on Ubuntu 24.04, follow this guide, which will help you install PHP 8.4 and configure it to work with both web servers.
Table of Contents
Step 1: Install Apache or Nginx
When choosing between Apache and Nginx for your web server on Ubuntu 24.04, it’s important to understand their key differences:
- Apache offers flexible configurations with
.htaccessfiles and a broad range of built-in features, making it ideal for complex setups and shared hosting environments. However, it can be less efficient in handling high traffic due to higher memory usage. - Nginx, on the other hand, excels in performance and scalability with its asynchronous, event-driven architecture, making it suitable for high-traffic sites and efficient resource management. It also works well as a reverse proxy or load balancer.
Recommendation: If you need advanced configurations and features, go with Apache. If you prioritize performance and efficiency, Nginx is the better choice. Alternatively, using Nginx as a reverse proxy in front of Apache combines the strengths of both servers.
Installing Apache on Ubuntu
First, it’s important to update your installed software package list to ensure that you have the latest information about available packages.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade -y
If you prefer to use Apache as your web server, install it using the following command:
sudo apt install apache2 -y
Installing Nginx on Ubuntu
For those who choose Nginx, install it with:
sudo apt install nginx -y
Installing PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu
Ubuntu 24.04 does not include PHP 8.4 in its default repositories, so you need to add the necessary repository to get the latest PHP version.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php sudo apt update sudo apt install php8.4 -y
Depending on your project needs, you may require additional PHP extensions. For example, if your project involves handling images, working with databases, or different data formats, you can install the relevant extensions.
sudo apt install php8.4 libapache2-mod-php8.4 php8.4-fpm php8.4-mysql php8.4-xml php8.4-mbstring php8.4-curl -y
Step 3: Switch Between PHP Versions (If Both 8.3 and 8.4 Are Installed)
If you already have PHP 8.3 installed on your system and want to use to PHP 8.4, you need to disable old php (PHP 8.3 module) and enable new php (PHP 8.4 module) using a2dismod and a2enmod commands.
sudo a2dismod php8.3 sudo a2enmod php8.4
Step 4: Configuring Apache to Use PHP 8.4
If you’ve installed Apache as your web server and want to use PHP 8.4, you need to activate the PHP module, which allows Apache to process PHP files and serve them correctly.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
To verify PHP is working with Apache, create a test PHP file:
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" | sudo tee /var/www/html/info.php
Now, open your web browser and navigate to the following URL, here you should see the PHP information page, confirming that PHP is correctly installed and configured.
http://your_server_ip/info.php
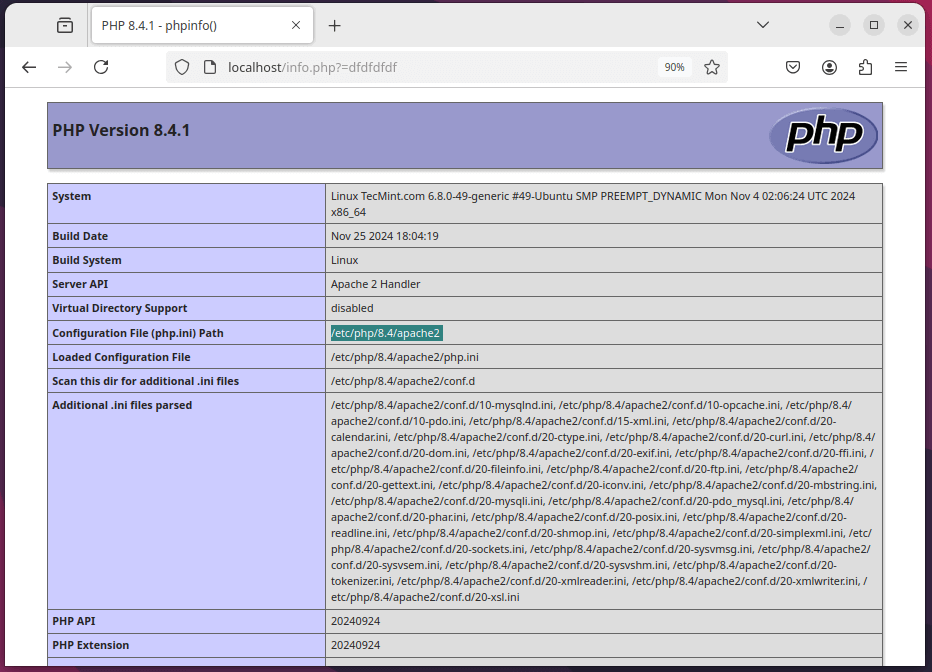
This will display the PHP information page, confirming that PHP 8.4 is correctly installed and configured.
Step 5: Configuring Nginx to Use PHP-FPM
When using Nginx as your web server, PHP is processed through PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager), which is a special service that handles PHP requests and runs them efficiently.
To configure Nginx to use PHP-FPM, you need to edit the default Nginx configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Look for the block that handles PHP files (it should be commented out) and modify it to look like this:
location ~ .php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock;
}
After making these changes, save the file and restart Nginx and PHP-FPM to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart nginx sudo systemctl restart php8.4-fpm
To verify PHP is working with Nginx, create a test PHP file similar to the Apache setup:
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" | sudo tee /var/www/html/info.php
Now, open your web browser and navigate to the following URL, here you should see the PHP information page, confirming that PHP is correctly installed and configured.
http://your_server_ip/info.php
Conclusion
You have successfully installed PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu 24.04 and configured it to work with both Apache and Nginx.
Make sure to remove the info.php file after testing, as it can expose sensitive information about your PHP configuration:
sudo rm /var/www/html/info.php
With PHP 8.4 installed, you can now explore its new features and improvements, enhancing your web development projects.