Pasteurization
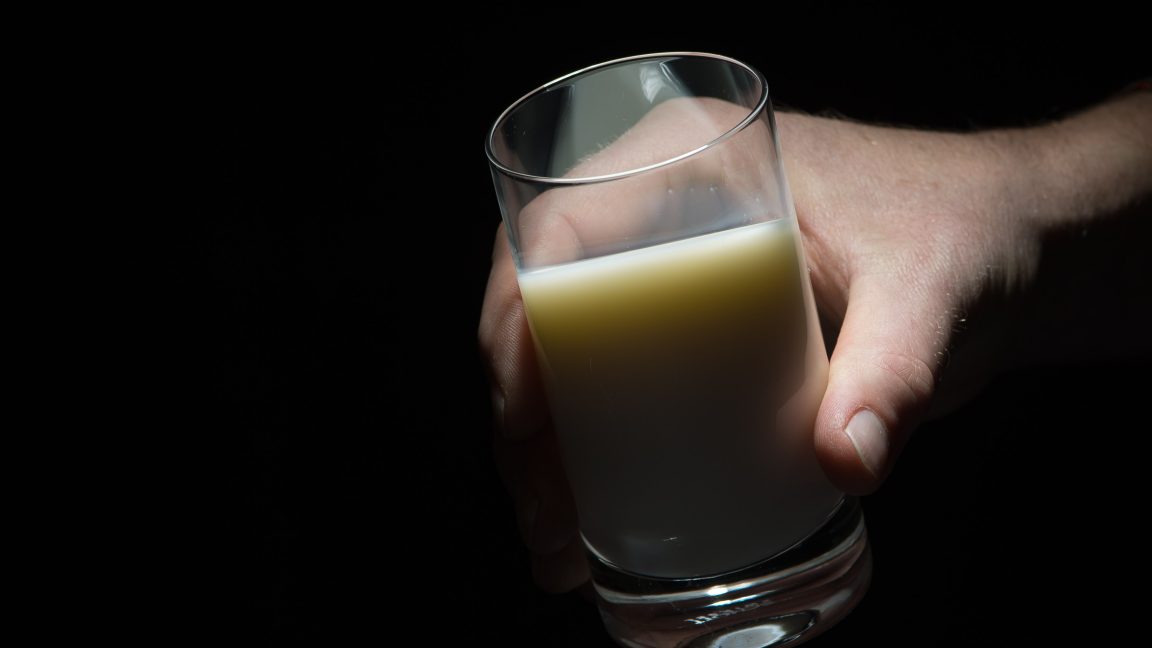
The milk-related risk of H5N1 is only from raw milk; pasteurized milk does not contain live virus and is safe to drink. Pasteurization, which heats milk to a specific temperature for a specified amount of time, kills a variety of bacteria and viruses, including bird flu. Influenza viruses, generally, are considered susceptible to heat treatments because they have an outer layer called an envelope, which can be destabilized by heat. Studies that have specifically looked at the effectiveness of heat-killing treatments against H5N1 have repeatedly found that pasteurization effectively inactivates the virus.
The advent of pasteurization is considered a public health triumph. Its adoption of a safe milk supply contributed to a dramatic reduction in infant deaths in the early 20th century. Before that, milkborne infections—including human and bovine tuberculosis, brucellosis, salmonellosis, streptococcal infections, diphtheria, and “summer diarrhea”—were common killers of infants.
As such, public health officials have long advised people against consuming raw milk, which has no evidence-based health benefits. Raw milk consumption, meanwhile, is linked to higher rates of outbreaks from pathogens including Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, toxin-producing E. coli, Brucella, Campylobacter, and many other bacteria.
Risky drinking
Since H5N1 was found spreading among dairy cows in March, health experts have warned about the additional risk of consuming raw milk. Still, consumption of raw milk has continued, and surprisingly increased, as supporters of the dangerous practice have accused health officials of “fearmongering.”
When the retail sampling of Raw Farm’s milk came back positive, the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) conducted testing at the company’s locations, which were negative for the virus. The CDFA will now begin testing Raw Farm’s milk for bird flu twice a week.
The recalled milk has lot code 20241109 and a “best by” date of November 27, 2024, printed on the packaging.
“Drinking or accidentally inhaling raw milk containing bird flu virus may lead to illness,” California’s public health department said. “In addition, touching your eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands after touching raw milk with bird flu virus may also lead to infection.”
Some US dairy workers who contracted the virus from infected cows reported having had milk splash in their eyes and face. A common symptom of H5N1 infections in humans during the dairy outbreak has been conjunctivitis, aka eye inflammation.